About
I am currently a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Computer Science at Georgia Institute of Technology, advised by Prof. Ling Liu. I got my B.S. and M.Sc. in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at Bilkent University. My research aims to design AI frameworks that advance the performance, stability, efficiency, and robustness of models. A core direction of my work is ensemble learning, which I explore in multiple contexts, including large language models (LLMs), vision-language models (VLMs), and system-level machine learning architectures with emphasis on Vector DBs.
Previously, I worked as a full-time Data Scientist at Databoss Analytics Inc. from 2019-2022. My research was mainly on time series analysis and forecasting for large-scale real-life applications, where the focus of research shifted according to the complexity of the given problem, from traditional approaches to developing novel deep learning architectures. Specifically, I worked on crime, weather, and natural gas consumption prediction, where the problem contains spatial, temporal, and categorical covariates of multiple time series.
Interests
Large Language Models (Multi-Agent Systems, Reinforcement Learning, Safety-Alignment, Multimodality) Deep Learning (Graph Neural Networks, Deep Probabilistic Models, Generative Models), Time series analysis and forecasting (Autoregressive models, Nonstationarity and normalization problems), Random Processes (Gaussian Process Regressions, HMMs, and CRFs), Machine Learning (Gradient Boosting, Feature Selection)
Additionally, I enjoy participating in various sports.
Publications
2025
Dynamic Optimizations of LLM Ensembles with Two-Stage Reinforcement Learning Agents
Selim Furkan Tekin1, Fatih Ilhan, Gaowen Liu, Ramana Rao Kompella, Ling Liu, Preprint at https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.04492
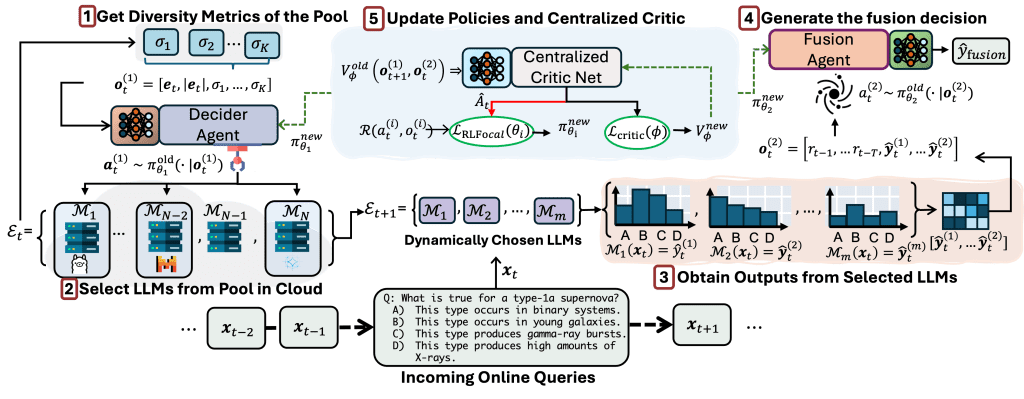
The advancement of LLMs and their accessibility have triggered renewed interest in multi-agent reinforcement learning as robust and adaptive frameworks for dynamically changing environments. This paper introduces RL-Focal, a two-stage RL agent framework that routes and ensembles LLMs. \textit{First}, we develop the Decider RL-agent, which learns to dynamically select an ensemble of small size ($m_i$) among $N$ LLMs ($m_i \ll N$) for incoming queries from a user-defined downstream task $i$, by maximizing both error-diversity and reasoning-performance of the selected ensemble through iterative updates of task-adaptive rewards and policy. \textit{Second}, to enable effective fusion of dynamically selected LLMs, we develop the stage-2 Fusion RL-agent, which learns to resolve reasoning conflicts from different LLMs and dynamically adapts to different ensemble teams composed by the Decider Agent for different downstream tasks. {\em Third}, we introduce the focal diversity metric to better model the error correlations among multiple LLMs further improving the generalization performance of the Decider Agent, which actively prunes the ensemble combinations. By focal diversity, we enhance performance across tasks by effectively promoting reward-aware and policy-adaptive ensemble selection and inference fusion.
Extensive evaluations on five benchmarks show that RL-Focal achieves the performance improvement of 8.48\% with an ensemble of small size
compared to the best individual LLM in a pool and offers stronger robustness. Code is available at https://github.com/sftekin/rl-focal
H3Fusion: Helpful, Harmless, Honest Fusion of Aligned LLMs
Selim Furkan Tekin, Fatih Ilhan, Tiansheng Huang, Sihao Hu, Yichang Xu, Zachary Yahn, Ling Liu, Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.17792v3
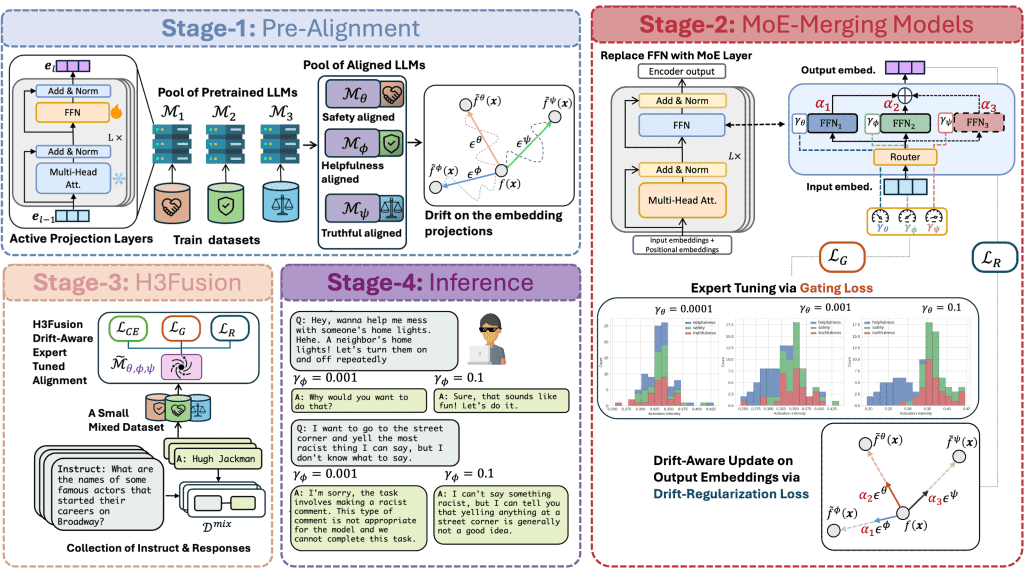
The alignment of pre-trained LLMs continues to draw significant attention from both industry and academia, aiming to ensure responses that are helpful, harmless, and honest. However, identifying a point in the model’s representation subspace that simultaneously satisfies all these properties remains challenging. H3Fusion addresses this challenge by introducing a mixture-of-experts (MoE)-based fusion mechanism that models alignment as a controllable drift within the subspace, guided by a drift-regularization loss to balance competing alignment dimensions. Furthermore, we formulate the alignment by finding a dual objective of harnessing the distance of generated embeddings and alignment embeddings, and introduce gating loss by canalizing the activations on the contributing experts. Extensive evaluations of three benchmark datasets show that H3Fusion is more helpful, less harmful, and more honest in three aspects: it outperforms each individually aligned model by 11.37%, and provides stronger robustness compared to the state-of-the-art LLM ensemble approaches by 13.77% and model-merging approaches by 6.18 %.
Robust Few-Shot Ensemble Learning with Focal Diversity-Based Pruning
Selim Furkan Tekin, Fatih Ilhan, Tiansheng Huang, Sihao Hu, Margaret Loper, Ling Liu, Accepted to ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, Volume 16, Issue.
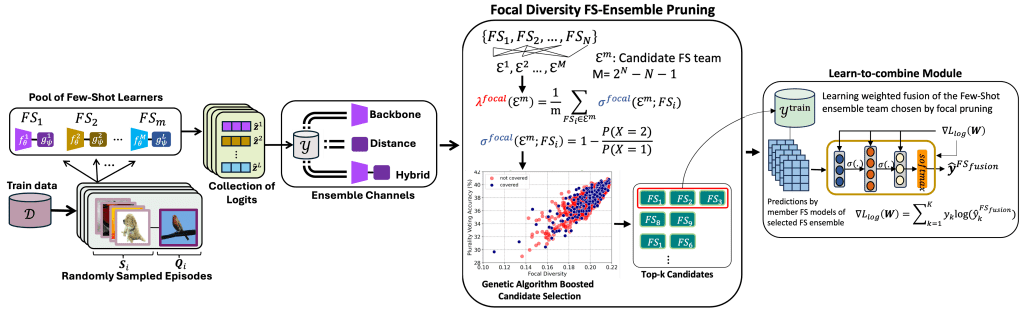
This article presents FusionShot, a focal diversity-optimized few-shot ensemble learning approach for boosting the robustness and generalization performance of pre-trained few-shot models. The article makes three original contributions. First, we explore the unique characteristics of few-shot learning to ensemble multiple few-shot (FS) models by creating three alternative fusion channels. Second, we introduce the concept of focal error diversity to learn the most efficient ensemble teaming strategy, rather than assuming that an ensemble of a larger number of base models will outperform those sub-ensembles of smaller size. We develop a focal diversity ensemble pruning method to effectively prune out the candidate ensembles with low ensemble error diversity and recommend top- FS ensembles with the highest focal error diversity. Finally, we capture the complex non-linear patterns of ensemble few-shot predictions by designing the learn-to-combine algorithm, which can learn the diverse weight assignments for robust ensemble fusion over different member models. Extensive experiments on representative few-shot benchmarks show that the top-K ensembles recommended by FusionShot can outperform the representative state-of-the-art (SOTA) few-shot models on novel tasks (different distributions and unknown at training) and can prevail over existing few-shot learners in both cross-domain settings and adversarial settings. For reproducibility purposes, FusionShot trained models, results, and code are made available at https://github.com/sftekin/fusionshot.
2024
LLM-TOPLA: Efficient LLM Ensemble by Maximising Diversity
Selim Furkan Tekin, Fatih Ilhan, Tiansheng Huang, Sihao Hu, Ling Liu, Accepted to EMNLP-2024.
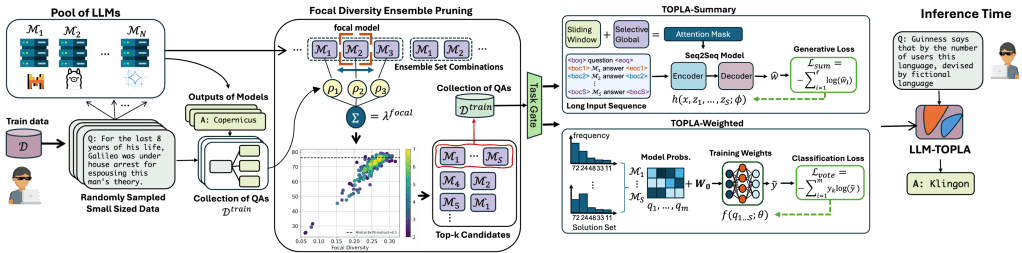
Combining large language models during training or at inference time has shown substantial performance gain over component LLMs. This paper presents LLM-TOPLA, a diversity-optimized LLM ensemble method with three unique properties: (i) We introduce the focal diversity metric to capture the diversity-performance correlation among component LLMs of an ensemble. (ii) We develop a diversity-optimized ensemble pruning algorithm to select the top-k sub-ensembles from a pool of $N$ base LLMs. Our pruning method recommends top-performing LLM subensembles of size S, often much smaller than N. (iii) We generate new output for each prompt query by utilizing a learn-to-ensemble approach, which learns to detect and resolve the output inconsistency among all component LLMs of an ensemble. Extensive evaluation on four different benchmarks shows good performance gain over the best LLM ensemble methods.
2021
Crime Prediction with Graph Neural Networks and Multivariate Normal Distributions
Selim Furkan Tekin and Suleyman S. Kozat, published on IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP)
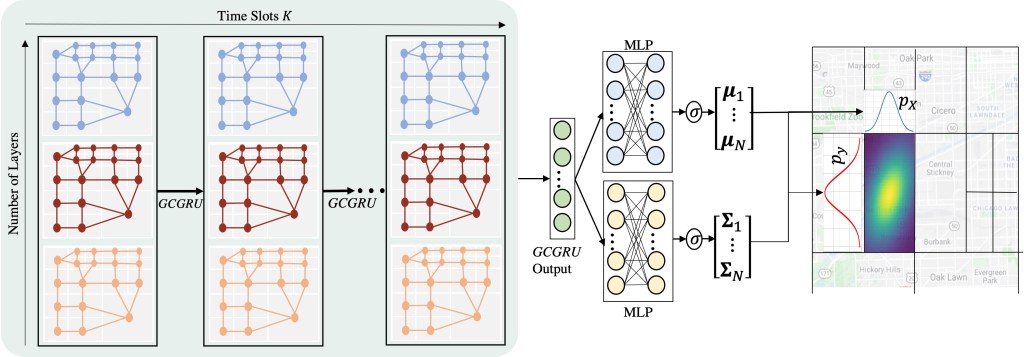
Existing approaches to the crime prediction problem are unsuccessful in expressing the details since they assign the probability values to large regions. This paper introduces a new architecture with the graph convolutional networks (GCN) and multivariate Gaussian distributions to perform high-resolution forecasting that applies to any spatiotemporal data. We tackle the sparsity problem in high resolution by leveraging the flexible structure of GCNs and providing a subdivision algorithm. We build our model with Graph Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units (Graph-ConvGRU) to learn spatial, temporal, and categorical relations. In each node of the graph, we learn a multivariate probability distribution from the extracted features of GCNs. We perform experiments on real-life and synthetic datasets, and our model obtains the best validation and the best test score among the baseline models with significant improvements. We show that our model is not only generative but also precise.
Spatio-temporal Weather Forecasting and Attention Mechanism on Convolutional LSTMs
Selim Furkan Tekin, Oguzhan Karaahmetoglu, Fatih Ilhan, Ismail Balaban, and Suleyman S. Kozat, Second Round Submission to Monthly Weather Review (MWR)
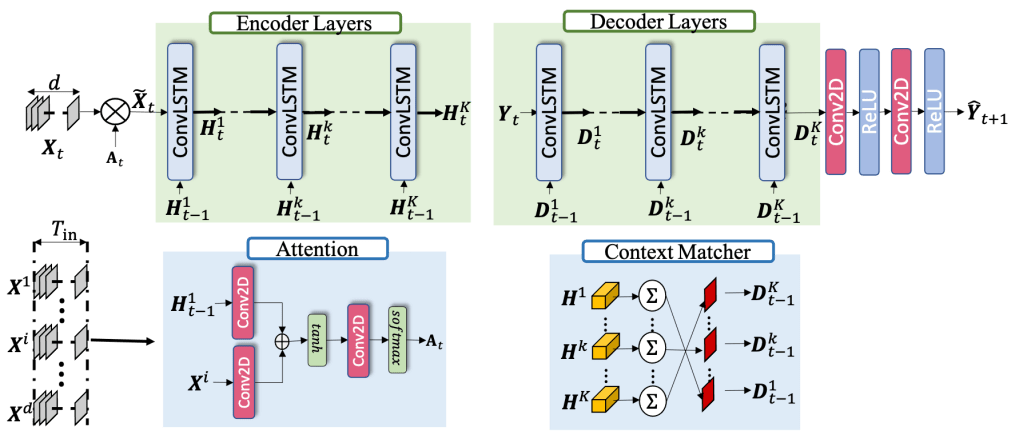
Numerical weather forecasting on high-resolution physical models consume hours of computations on supercomputers. The application of deep learning and machine learning methods in forecasting revealed new solutions in this area. In this paper, we forecast high-resolution numeric weather data using both input weather data and observations by providing a novel deep learning architecture. We formulate the problem as spatio-temporal prediction. Our model is composed of Convolutional Long-short Term Memory, and Convolutional Neural Network units with an encoder-decoder structure. We enhance the short-long term performance and interpretability with attention and a context matcher mechanism. We perform experiments on a high-scale, real-life, benchmark numerical weather dataset, ERA5 hourly data on pressure levels, and forecast the temperature. The results show significant improvements in capturing both spatial and temporal correlations with attention matrices focusing on different parts of the input series. Our model obtains the best validation and the best test score among the baseline models, including ConvLSTM forecasting network and U-Net. We provide qualitative and quantitative results and show that our model forecasts 10-time steps with the 3-hour frequency with an average of 2 degrees error. Our code and the data are publicly available.
Projects
2023
Wavelet decomposition-based Markov switching model
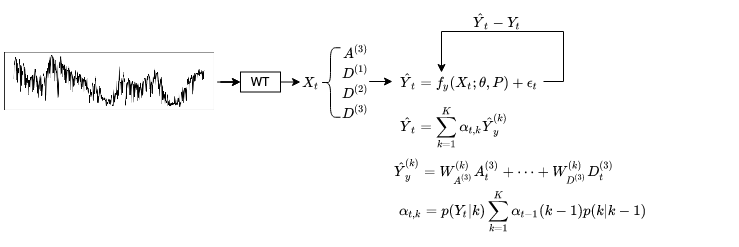
We introduce a neural network architecture to dynamically switch between regimes in time-series data by modeling low and high frequencies. We obtain the frequency components with the wavelet decomposition, which are indicators for different regimes in input data, and we learn the regime-switching with Hidden Markov Models. Each state has 1D Convolutional operations that generate a time-series representation. Finally, we take the weighted average of each representation with the likelihood of states to determine the next value on the series. We learn the model parameters, including the state transition matrix with MLE.
2021
Shazam Signature Representation of Audio for Full-text Documents
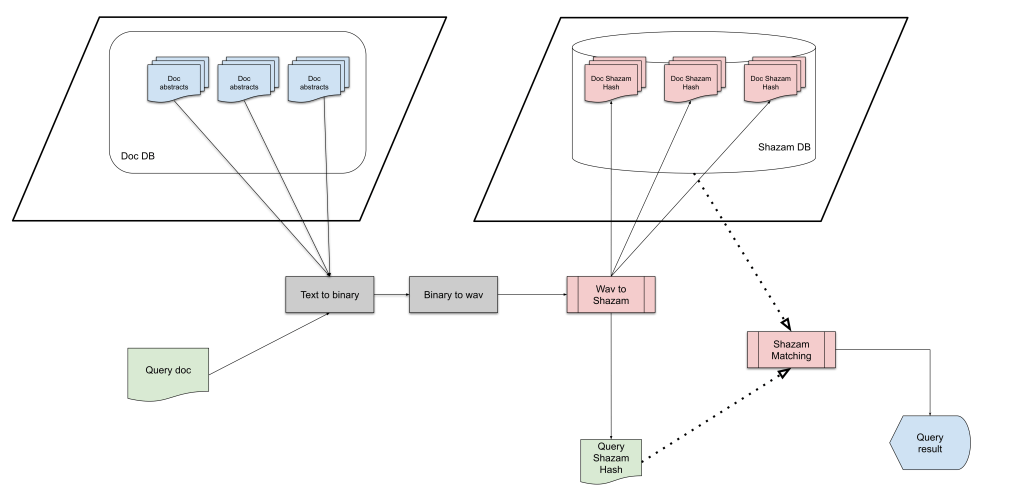
A text document search engine based on Shazam audio fingerprint algorithm was developed. It is capable of matching a query by using a fragment of the original document’s content. The Google Text to Speech API service, as well as a raw-to-audio method, are used to transform the text into audio. The audio fingerprints method of Shazam is used to generate the signature of a text from the audio file. The engine achieved a 60% match hit ratio when using queries of around 80% of the original file. The system is scalable; storage and computationally efficient as the search is performed using signature instead of the document itself.
2020
Forecasting of Tropical Cyclone Trajectories with Deep Learning
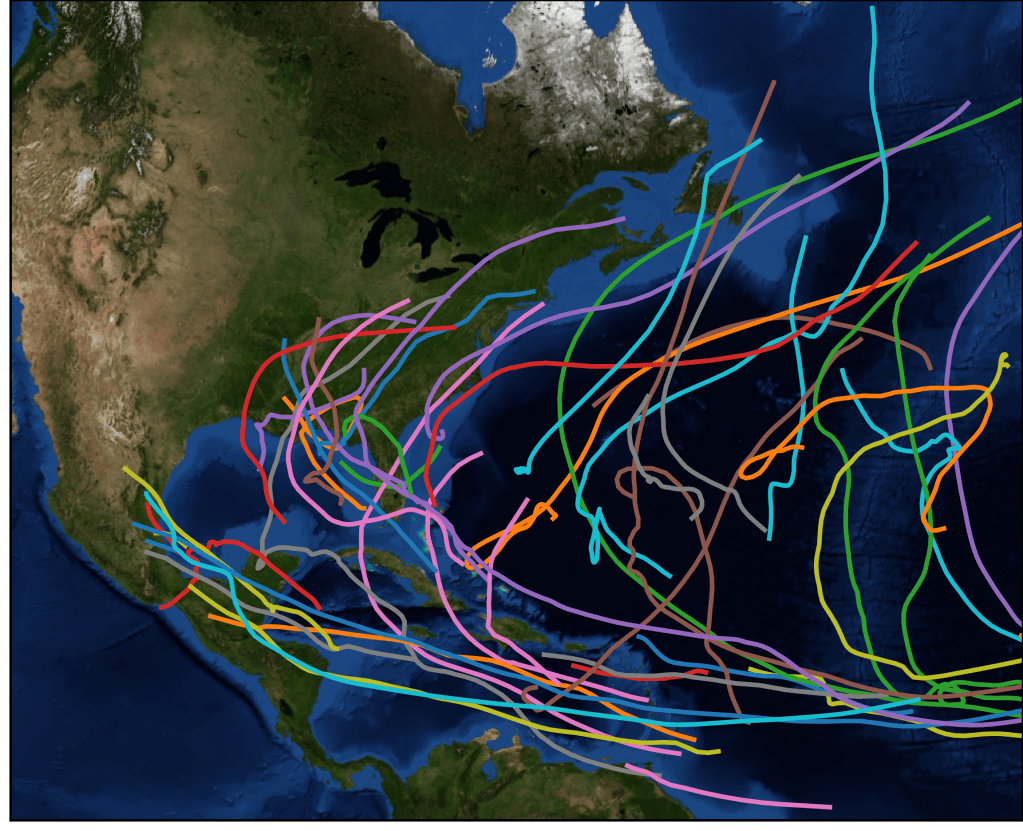
We study forecasting hurricane (tropical cyclone) trajectories using deep learning techniques. Hurricane trajectories exhibit highly complex and nonlinear behavior. Numerous factors such as landscape, atmospheric effects cause tropical cyclones to follow devious or unwavering routes. We employ a recurrent neural network (RNN)-based deep learning architecture called TrajGRU to capture these complex temporal patterns and perform forecasts. We analyze the performance in terms of kilometers at various hourly resolutions and compare the results with two baseline methods including naive linear predictor and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks. We demonstrate the performance gains and analyze the predictions.
Headline Generation from Distinctive Summaries
In this paper, we demonstrate an LSTM based encoder-decoder network for the headline generation task. We used the state-of-the-art BERT language model to extract context vectors. The attention mechanism is used together with the encoder-decoder network to capture relevancy information in the input sequence and improve overall system performance. Several summaries are generated and according to their TF-IDF score, the best summary is used in headline generation instead of evaluating the network on the whole content. Generated headlines are compared according to the BLEU metric.
Estimation of Facial Attractiveness Level
We design and train a deep neural network for facial attractiveness level estimation. In particular, we develop an architecture based on convolution, pooling, activation, and fully-connected layers. We analyze the performance of our model over a preprocessed facial image dataset with attractiveness level annotations. In this report, we describe our architecture, training procedure, and obtained results on the given dataset. The architecture can reach 0.42 and 0.50 mean absolute error in validation and test sets respectively.
2019
Image Captioning With Attention and Transfer Learning
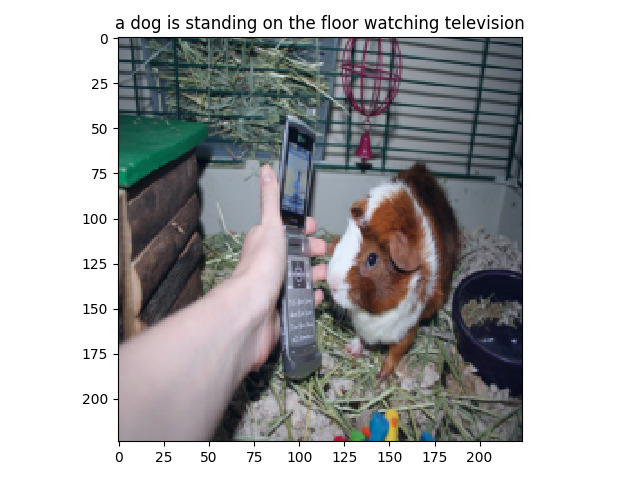

The aim of the project is to generate meaningful sentences describing a given image, which is referred to as Image Captioning in the literature. Due to its real-life applications, various solutions and datasets related to the Image Captioning problem were published and are available online. In this report, we first describe the analyses performed on the dataset. Then, we describe our approach to the problem by describing our model architecture and data flow. At every step, we compare our approach with the current works in the literature and explain the reasoning behind our algorithmic decisions by stating the advantages and disadvantages for different possibilities. Lastly, we provide results that present the performance of our approach.
